(PPE) PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENTS
SCISSOR AND FORCEPS, Spirit swab bowel
THERMOMETER
AUTOCLAVE & Sterlizer or Incubator
Dropper and Bottle
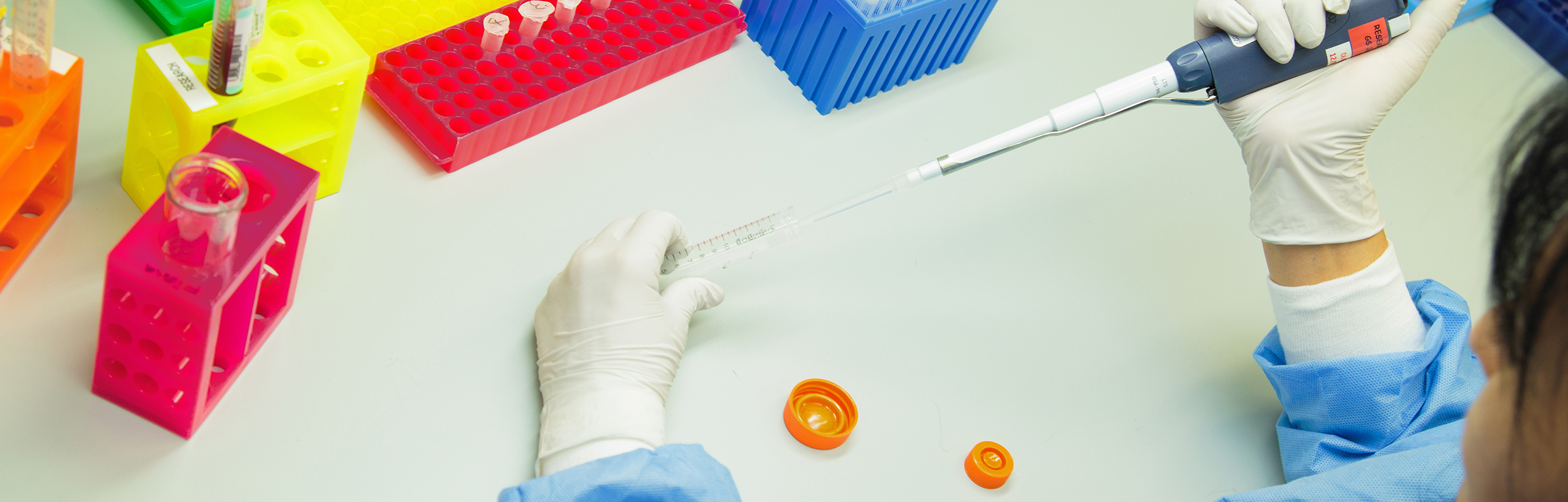
Pipettes
Pasteur pipette
Test Tubes and tube racks
WASH BOTTLE
CENTRIFUGE
BALANCE
BLOOD DONATION CHAIR
BLOOD SHAKER
BLOOD BAGS
PACKING AND LABEL
REFRIGERATOR CENTRIFUGE FOR SEPARATE BLOOD COMPONENTS
PLASMA EXTRACTOR /SEPRATOR/EXTRACTOR
BLOOD BAG TUBE SEALER
REFRIGERATOR AND BLOOD STORAGE
BLOOD BANK REFRIGERATOR
PLASMA FREEZER STORAGE
DEEP FREEZER
Platelet agitator and incubator
Temperature controlled boxes for transportation of blood components
Water bath FOR INCUBATION
Microscope
Microscope Slide and Cover Slip
WASTE SEGREGATION
(PPE) PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENTS